What is ALARP in Floor Safety
Wherever possible, a business, manager, or owner is recommended by the UK HSE and the UK Laws on Floor Safety to have floors that are safe from slips, trips and falls to keep persons safe.
This typically means if a floor is likely to become wet or contaminated in use and the mitigation to clean or offset this issue can not be easily or practicably met, then a floor, should give values when Pendulum Tested WET or CONTAMINATED (with substances relevant to that floor surface) a Pendulum Test Value of 36 PTV on a horizontal surface Increasing By 1.75 Degrees for Every 1 Degree Of Slope.
If, however, the floor can not meet this value of 36 PTV but it can be demonstrated properly, repeatedly and consistently that a floor, if it becomes wet or contaminated will be immediately addressed (such as cordoning off, cleaning and drying) then it ‘might’ be argued that ALARP has been met.
ALARP stands for ‘As Low as Reasonably Practicable’
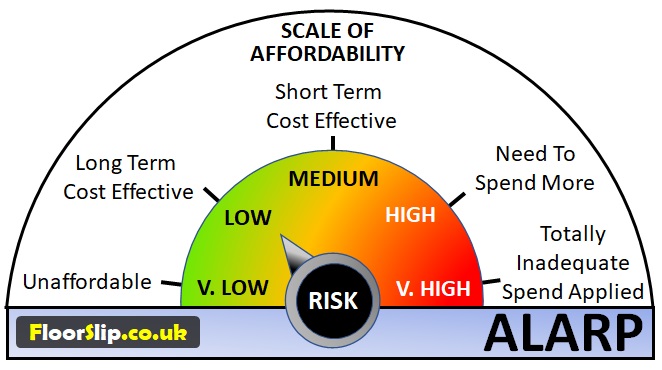
ALARP, is used and promoted by the HSE and means that all reasonable effort has been applied to ensure a floor is safe and ‘holistic’ factors have been considered and applied such as: - monitoring / testing of floor surfaces; training in safety and risk; fast effective reaction to spills; effective cleaning; effective matting; suitable lighting; non-slip coatings; preventing environmental ingress and contaminants etc. and the cost involved in reducing the risk further would be grossly disproportionate to the benefit gained. The image above simply portrays this meaning; it is a balance of cost against risk.
A policy that considers these factors from a holistic ALARP viewpoint could be considered as reasonably robust in providing a relatively safe floor environment, even if the floor itself is unable to provide the ‘recommended’ 36PTV when wet on a horizontal floor. See Buying / Specifying Floors
The table below are GENERIC EXAMPLES of how ALARP might be considered / applied…
Have the following factors been CONSIDERED?
Physical Aspects of ALARP
Provision of a floor that meets or exceeds 36 PTV when wet or contaminated
CONTROL (Examples) - Change of floor, Anti-slip coatings, Pendulum Testing and Surface Roughness Monitoring
Weather Ingress (On Clothing and Umbrellas, Prams, baskets and trolleys, Vehicles and fork lift trucks etc.)
CONTROL (Examples) - Mats, Canopies
Trip hazards and obstructions
CONTROL (Examples) - Housekeeping Policy
Wet contaminants (water, motor oil, diesel, cooking oil, perfume, shower products etc)
CONTROL (Examples) - Cleaning, Spills Recovery
Dry Contaminants (Talc, flour, salt, swarf, dust etc.)
CONTROL (Examples) - Cleaning, Spills Recovery
Floor slopes - Each 1 degree of slope above horizontal requires an additional 1.75 PTV
CONTROL (Examples) - Limit Angles to less than 5 degrees; Increase floor PTV values
Condition / wear of floor
CONTROL (Examples) - Cleaning, Repairing, Replacing
Control of Footwear
CONTROL (Examples) - Cleaning, Replacing, Policy, Using STAR Rated / GRIP Anti-slip shoes
Age and disability
CONTROL (Examples) - Ramps and Slopes, Lifts, Wheelchair access
Behaviour of staff and visitors
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Awareness, Training, Warninsg, Signs
Attitude Aspects of ALARP
Unaware of floor safety
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Awareness, Training
Inebriation and the effects of chemical substances
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Awareness, Training
Management Aspects of ALARP (Often a Key Problem)
A misplaced attitude to Aesthetics over Safe floors and Safety in general
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Education
Blind Acceptance that if manufacturers, websites and sales publications use the term ‘non-slip’ that it must meet all circumstances but do not prove the claim by testing or obtaining test certificates for products supplied.
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Education, Testing
Lack of understanding or niaivety of floor safety
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Education
No awareness or knowledge of the effects of floor slopes on slip safety
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Education
Failing to Inspect / Inadequate Inspections
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Education
Failing to conduct, plan or exceute Risk assessments / Inadequate Risk Assessments / In-house assessments can miss areas
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Education, Training, Actually doing one!
Reaction to spills - urgency, inadequate or no cleaning apparatus, training
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Education, Preparation, Awareness
Inadequate Lighting hiding / masking slip / trip hazards.
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Education, Testing
Floor replacement programs and non-slip solutions not considered, planned or executed
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Education, Testing
Nil or inadequate assessments to correct for known hazards
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Education, Testing
Inadequate cleaning regimes
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Education, Training, Timing, Equipment
Monitoring of potential slip hazards, awareness of what they might be
CONTROL (Examples) - Policy, Education, Training, Testing